Associate Professor and Extension Economist –Management and Policy
Outline of Presentation
- Where We Are and Next Steps
- General Overview
- Base and Yield Updating
- Direct and Counter-cyclical Payments
- Payment Limitations
- Peanuts
- Conservation Program Changes
- WTO Issues/Impacts
- What Do You Need to Do?
- Available Extension Resources
- Question and Answer Session
Where We Are and Next Steps
- Commodity program sign up for crop years 2002 and 2003 announced for October 1st – June 2, 2003
- FSA has sent letters with planted acreage histories
- FSA has some information on yields
- Disaster, NAP, LDPs
- You have to provide any additional information on yields – if needed
- Crop insurance information will be allowable if accompanied by supporting documentation
- Base & Yield Updating ends March 31st
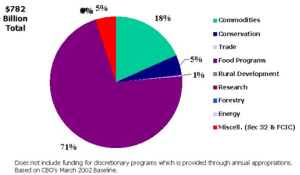
General Overview
- 6 year farm bill beginning in 2002 and ending in 2007
- Comprehensive bill covering:
- Commodity programs
- Conservation
- Trade
- Nutrition Programs
- Credit
- Rural Development
- Research and Related Matters
- Forestry
- Energy
- Miscellaneous
- Will be required to sign-up every year
- Different from 1996 farm bill
- Implications for budget conciliation legislation
General Overview (Cont.)
- Commodity provisions similar to previous programs
- Continue direct “AMTA” payments
- Continue marketing loan gains/LDPs
- No production controls
- Initiate counter-cyclical payments (CCPs)
- Similar to target price/deficiency payment program
- Allows update of bases and program yields
- Major changes for Soybeans and Peanuts
- Provisions similar to other program crops
General Overview (Cont.)
- Requires country-of-origin labeling for meat, fish, produce and peanuts by 2004
- Meat products would be stamped U.S. made only if the animals were born, raised, and slaughtered in the U.S.
- Proposed packer ownership ban was dropped
- House and Senate will hold hearings and investigate further
- Food stamp benefits restored for legal immigrants who have been in the U.S. for 5 years
- Did not include Cuba trade provision
- Would have allowed private U.S. financing of ag products to Cuba
General Overview (Cont.)
- Added an Energy Title
- Commits $405 million to the development of resources for the production of ethanol and biodiesel facilities
- Initiates a counter-cyclical dairy program
- Wool and Mohair provided marketing loan benefits
- Honey provided marketing loan benefits
- Added new Conservation Security Program
- EQIP funding increased 6 fold
- Includes authority for LDPs on grazed wheat, oats, barley and triticale
Allocation of U.S. Budget Outlays by Function, FY 2001

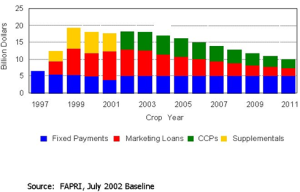
CCC Net Expenditures

U.S. Crop Prices

Conservation Program Expenditures

Definitions
- Covered Crops:
- Wheat, corn, grain sorghum, barley, oats, upland cotton, rice, soybeans, and other oilseeds (sunflower seed, rapeseed, canola, safflower, flaxseed, mustard seed, or if designated by the Secretary, another oilseed).
- Does not include crambe and sesame seed
- Loan Commodities:
- Covered commodities plus extra long staple cotton, wool, mohair, honey, dry peas, lentils, and small chickpeas.
Crop Base Updating
- Current covered crops have three choices:
- Retain current AMTA bases
- Retain current AMTA base and add oilseeds (if applicable)
- Update bases by using 1998-2001 planted and considered planted acreage for all crops
- Base updating will be on a farm (FSA farm number) by farm basis
- This decision needs to be made considering farm program yield alternatives
- Fixed and counter-cyclical payments made on 85% of crop base
- Peanuts a little different
Base Updating Example: FSA farm #111
- Current base acres
- Cotton 128 acres
- Wheat 32 acres
- Planted acres 1998 1999 2000 2001
- Cotton 160 128 160 128
- Wheat 0 32 0 32
- 2002-2007 Base acre options:
- Use current base acres
Cotton 128 acres
Wheat 32 acres or - Update using 1998 – 2001 average planted acres
Cotton 144 acres
Wheat 16 acres
- Use current base acres
Base Updating Example: FSA farm #112
- Current base acres
- Cotton 128 acres
- Wheat 32 acres
- Soybeans n/a
- Planted acres 1998 1999 2000 2001
- Cotton 128 80 80 80
- Wheat 32 0 0 0
- Soybeans 0 80 80 80
- 2002-2007 Base acre options:
- Keep current base acres
- Use current base acres plus oilseeds
Cotton 100 acres
Wheat 0 acres
Soybeans 60 acres or - Update using 1998 – 2001 average planted acres
Cotton 92 acres
Wheat 8 acres
Soybeans 60 acres
Farm Program Yield Updating
- Only applies to counter-cyclical payment
- Only allowed if update base acres using 1998-2001 planted acreage
- Producers have three choices:
- Retain current program yields
- Update yields by adding 70% of the 1998-2001 average yield (excluding any year planted acreage was zero) minus current program yields to the current program yield
- Update yields by taking 93.5% of 1998-2001 yields, excluding any year planted acreage was zero
- 1998-01 yields will be weighted average over period (weighted by planted acres each year)
Farm Program Yield Updating (Cont.)
- Can replace any of the 1998-2001 yields with 75% of the county average for that year
- Using 75% of 1998-01 county average yield per harvested acres to replace any yield
- Yield updating will be on a crop by crop basis for each FSA farm #
- All crops on a farm are required to use the same method for determining yields
Farm Program Yield Updating
Example: Cotton
- Current farm program yield 500 lbs
- 1998-2001 average yield 725 lbs
- 2002 Yield Options:
- FPY = 500
- FPY = 500 + ((725 – 500) x .70)) = 657.5
- FPY = (725 x .935) = 677.88
Non-program or Wildcat Acres
- Refers to cropland used in the production of a covered commodity over the 1998 to 2001 period that was not receiving PFC payments provided for in the 1996 Farm Bill
- This is land that has not been “in the program” from 1996 to 2002
- If a producer chooses to update base acres then this land can be added during signup
- Will have to prove acres
- Program yields for the purposes of calculating direct payments will be assigned to these acres
- Law states that yields for similar farms in the area will be used
- The County Committee will assign a yield based on yields for 3 similar farms in the count
- Program yield used for calculating the CCP can be “updated” using proven yields over the 1998 to 2001 period and choices discussed earlier
Soybean and Other Oilseeds
- Brings soybeans and other under same provisions as other program crops
- Payment yield establishment
- Average yield per planted acre over the 1998-2001 period excluding any year planted acreage was zero
- Can replace low yields in the 1998-2001 period with 75% of the county yield
- Yield ratio is the ratio resulting from dividing the national average yield for the oilseed for the 1981-85 crops by the national average yield for the 1998-01 crops
- Payment yield = average yield x yield ratio
- Can update yield for counter-cyclical payment purposes
- Provides same three option given other crops
Direct Payments
- Can choose to update base but will use current AMTA yield
- Soybeans and peanuts different
- Same formula
- Direct Payment = (payment rate x (base acres x .85) x farm program yield)
- Timing
- 2002 as soon as practical after enactment
- 2003-2007 not before October 1 of the calendar year in which the crop of the covered commodity is harvested
- Advance Payments
- Producer Option
- For 2003-2007 up to 50% in any month between December 1 of the year before and October 1 (date payment is otherwise made)
Counter-Cyclical Payments
- Commodity specific based off of national price trigger
- Base owners and/or producers will receive a payment that depends on the effective price for the commodity:
- Target price
- Effective price
- Counter-cyclical payment rate ($/unit)
- CCP = CCP rate x (Base acres x .85) x Updated FPY
- Effective price equals the direct payment rate plus the higher of the market price or loan rate
- The national market price is the 12 month marketing year average for the crop (likely to be weighted average)
- Decoupled from production decision
Commodity Marketing Years
- Wheat, barley, oats, canola, rapeseed, and flaxseed
- June of year crop is harvested through next May
- Corn, sorghum, soybeans, sunflower seed, safflower, and mustard seed
- September of year crop is harvested through next August
- Upland cotton, rice, and peanuts
- August of year crop is harvested through next July
Counter-Cyclical Payments (Cont.)
- Won’t know for sure what total payment will be until end of marketing year
- This will be roughly a year after harvest
- If Secretary determines CCPs are required:
- 2002 – 2006 Payment Timing
- Producer can elect to receive up to 35% of the projected counter- cyclical payment in October of the year the crop is harvested
- An additional 35% beginning in February of the following year
- The balance after the end of the 12 month marketing year for the crop
- 2007 Payment Timing
- First payment (40%) after 6 months of marketing year
- Final payment after the end of the 12 month marketing year for the crop
- 2002 – 2006 Payment Timing
Other Crop Provisions
- Continues full planting flexibility on crop acreage bases other than:
- Limits on fruits and vegetables (other than lentils, mung beans, and dry peas)
- Continues conservation compliance
Other Crop Provisions (Cont.)
- GRAZE-OUT payments in lieu of LDPs for wheat, barley, and oats used for grazing livestock
- Producer enters into agreement with the Secretary to forgo harvesting
- Payment quantity determined by multiplying the quantity of grazed acreage and the payment yield in effect for the direct payment on the farm
- GRAZE-OUT payments for triticale
- Uses LDP rate for wheat
- Uses payment yield in effect for wheat direct payments
- Producer agrees to forgo any other harvesting of the commodity on the acreage
- Producer retains beneficial interest through the date the crop is grazed out
- Application Period
- Begins on the first day of mechanical harvest as determined by the county committee
- Ends on March 31st of the calendar year after the year the crop is normally harvested
Other Crop Provisions (Cont.)
- GRAZE-OUT Payment Program Cont.
- Applications cannot be cancelled or withdrawn once requested
- If producer elects to use for grazing in lieu of harvesting, the crop shall not be eligible for:
- Any other marketing assistance loans or LDPs
- A crop insurance indemnity for the crop
- Noninsured crop assistance (NAP)
- Producers who lease cropland to a second party for grazing on a gain or per head per month basis only are NOT considered to have lost beneficial interest
- Note: producers are not eligible if crop is leased to a third party for grazing on a flat per acre rate
- Any producer or number of producers who share in the grazing of the acreage are eligible
- LDPs available for producers of hay and silage
- Derived from covered commodities
Direct Payments
|
Crops
|
1996 Farm Bill
2002 Rate |
2002 Farm Bill
2002-07 Rate |
|
Corn ($/bu)
|
0.261
|
0.28
|
|
Sorghum ($/bu)
|
0.314
|
0.35
|
|
Wheat ($/bu)
|
0.461
|
0.52
|
|
Upland Cotton ($/bu)
|
0.0572
|
0.0667
|
|
Rice ($/cwt)
|
2.05
|
2.35
|
|
Barley ($/bu)
|
0.202
|
0.24
|
|
Oats ($/bu)
|
0.022
|
0.024
|
|
Soybeans ($/bu)
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
Minor Oilseeds ($/lb)
|
N/A
|
0.0080
|
|
Peanuts ($/ton)
|
N/A
|
36
|
Loan Rates
|
Crops
|
1996 Farm Bill
2001 Rate |
2002 Farm Bill
2002-03 Rate |
2002 Farm Bill
2004-07 Rate |
|
Corn ($/bu)
|
1.89
|
1.98
|
1.95
|
|
Sorghum ($/bu)
|
1.71
|
1.98
|
1.95
|
|
Wheat ($/bu)
|
2.58
|
2.80
|
2.75
|
|
Upland Cotton ($/lb)
|
0.5192
|
0.52
|
0.52
|
|
Rice ($/cwt)
|
6.50
|
6.50
|
6.50
|
|
Barley ($/bu)
|
1.65
|
1.88
|
1.85
|
|
Oats ($/bu)
|
1.21
|
1.35
|
1.33
|
|
Soybeans ($/bu)
|
5.26
|
5.00
|
5.00
|
|
Minor Oilseeds ($/lbs)
|
0.093
|
0.096
|
0.093
|
|
Peanuts ($/ton)
|
N/A
|
355.0
|
355.0
|
|
Dry Peas ($/cwt)
|
N/A
|
6.33
|
6.22
|
|
Lentils ($/cwt)
|
N/A
|
11.94
|
11.72
|
|
Small Chickpeas ($/cwt)
|
N/A
|
7.56
|
7.43
|
- Wheat loan rates will be announced by class: hard red spring, hard red winter, soft red winter, soft white wheat, and durum.
Oilseed Load Rates
|
Crops
|
2002 Farm Bill
2002-03 Rate |
|
Oil- Type sunflower ($/lb)
|
0.0915
|
|
Other- Type sunflower ($/lb)
|
0.1210
|
|
Flaxseed ($/lb)
|
0.0698
|
|
Canola ($/lb)
|
0.0949
|
|
Rapeseed ($/lb)
|
0.0947
|
|
Safflower Seed ($/lb)
|
0.1253
|
|
Mustard Seed ($/lb)
|
0.0988
|
Loan Rates
- USDA has used the increase in most loan rates to adjust county loan rate differentials
- The new rates have been announced and there are already calls for their change








Target Prices
|
Crops
|
2002-2003
|
2004-2007
|
|
Corn ($/bu)
|
2.60
|
2.63
|
|
Sorghum ($/bu)
|
2.54
|
2.57
|
|
Wheat ($/bu)
|
3.86
|
3.92
|
|
Upland Cotton ($/lb)
|
0.724
|
0.724
|
|
Rice ($/cwt)
|
10.50
|
10.50
|
|
Barley ($/bu)
|
2.21
|
2.24
|
|
Oats ($/bu)
|
1.40
|
1.44
|
|
Soybeans ($/bu)
|
5.80
|
5.80
|
|
Minor Oilseeds ($/lb)
|
0.0980
|
0.1010
|
|
Peanuts ($/ton)
|
495.0
|
495.0
|
Distribution of Government Support
Example: Cotton

Distribution of Government Support
Example: Corn

Distribution of Government Support
Example: Grain Sorghum

Distribution of Government Support
Example: Wheat

Distribution of Government Support
Example: Rice

Distribution of Government Support
Example: Peanuts

Distribution of Government Support
Example: Soybeans

Probability that CC Payments for Cotton are Zero or Max, 2002-2007

Probability that CC Payments for Corn are Zero or Max, 2002-2007

Probability that CC Payments for Rice are Zero or Max, 2002-2007

Probability that CC Payments for Sorghum are Zero or Max, 2002-2007

Probability that CC Payments for Soybeans are Zero or Max, 2002-2007

Probability that CC Payments for Wheat are Zero or Max, 2002-2007

Probability that CC Payments for Peanuts are Zero or Max, 2002-2007

Payment Limitations
- Establishes individual payment limitations for direct payments, counter-cyclical payments, and marketing loan gains and/or loan deficiency payments
- Continues 3-entity rule
- Allows a producer to get 1 full limit and one-half of two others from different entities
- Marketing loan gains and/or Loan Deficiency Payments
- Can continue to use generic marketing certificates
- Effectively removes $75,000 limit
- Can continue to use generic marketing certificates
Seperate Sets of Limits
|
Covered Commodities-1
|
Peanuts
|
Wool, Mohair, and Honey
|
|
|
Direct Payments
|
$40,000
|
$40,000
|
N/A
|
|
Countercyclical payments
|
$65,000
|
$65,000
|
N/A
|
|
MLGs/LDPs-2
|
$75,000
|
$75,000
|
|
1. Covered Commodities are: wheat, corn, grain sorghum, barley, oats, upland cotton, rice, soybeans, and other oilseeds (sunflower seed, rapeseed, canola, safflower, flaxseed, mustard seed, or if designated by the Secretary, another oilseed).
2. Loan Commodities are: covered commodities plus extra long staple cotton, wool, mohair, honey, dry peas, lentils, and small chickpeas.
Payment Limitations (Cont.)
- Adjusted Gross Income Limitation
- Defined as: the 3 year average of the adjusted gross income or comparable measure of the individual or entity over the 3 preceding years
- Begins in 2003
- $2.5 million limit
- Unless not less than 75% of AGI comes from farming, ranching, or forestry operations
- An individual or entity shall not be eligible to receive any benefit (direct payments, counter-cyclical payments, and marketing loan gains/LDPs)
- Certification: An individual or entity shall provide to the Secretary
- Certification from a CPA or another third party
- Information and documentation through other procedures established by the Secretary
- Creates a new commission to study and make recommendations regarding payment limits
Payment Timeline for Most Commodities

Peanut Program
- Eliminates quota system
- Brings peanuts under same provisions as other program crops
- Bases and yields calculated over 1998-2001 period
- Will use calculated bases and yields for both direct and CCP payments
- Peanut producers will be eligible for:
- Fixed payments
- Counter-cyclical payments
- Marketing loan/LDPs
- Quota owners receive a quota buyout based off of 2001 quota levels (accounting for sales or transfers)
- $0.11/lb per year for 5 years or lump sum
- Lump sum can be taken in any year (2002-2007)
- Quota owners need to consider tax implications before choosing
- Yet to be determined whether quota buyout payment is ordinary income or capital gain
Peanut Program (Cont.)
- For 2002 payments, refers to historic peanut producer
- Average yield (1998 – 2001) period excluding any year peanuts were not planted
- May elect to replace up to 3 yields over the period with the 1990 to 1997 county average
- Average acreage (1998 – 2001) period including all 4 years and zeros in average
- Average yield (1998 – 2001) period excluding any year peanuts were not planted
- Producers will have until March 31, 2003 to assign the average yield and acreage to cropland on that farm or another farm in the same State or a contiguous state, subject to:
- Producer grew peanuts in State at least 1 year over 1998- 2001 period
- As of March 31, 2003, the producer is a producer on a farm in that State
Peanut Program (Cont.)
- Direct payments
- Timing
- 2002 as soon as practical after enactment
- 2003-2007 not later than September 30 of the calendar year in which the crop is harvested
- Timing
- Advance payments
- At producer option, for 2003-2007 up to 50% in any month between December 1 of the year before and September 30 (date payment is otherwise made)
- CCP payment timing
- 2002 – 2006
- First partial shall be made not earlier than in October 1 and not later than October 31 of the calendar year the crop is harvested
- Second partial not earlier than February 1 of the following year
- The balance after the end of the 12 month marketing year for the crop
- 2007 Payment Timing
- First payment after 6 months of marketing year
- Final payment after the end of the 12 month marketing year for the crop
- 2002 – 2006
Peanut Program (Cont.)
- CCP Partial Payment Amounts
- 2002 crop year (made to historic producers)
- First partial payment may not exceed 35%
- Second partial payment not to exceed 70% of revised estimate minus first payment
- Final payment actual payment minus first and second partial payments
- 2003 – 2006 crop years (made to base holders)
- First partial payment may not exceed 35%
- Second partial payment not to exceed 70% of revised estimate minus first payment
- Final payment actual payment minus first and second partial payments
- 2007 crop year
- First partial payment may not exceed 40%
- Final payment actual payment minus the first partial payment
- 2002 crop year (made to historic producers)
Peanut Program (Cont.)
- What I have been told recently
- 2002
- Quota buy out payments made
- Historic producers (1998-2001) receive direct and CCP payments
- 2002 peanut producers will be eligible for marketing loan gains or LDPs
- Will not be able to assign base acres for 2002
- 2003 Signup quite possibly the same time as 2002 signup
- Can start assigning base acres
- Will still have until March 31, 2003 to assign
- 2002
- Payments won’t likely be held back due to lawsuit
Honey Program
- Provides a marketing loan or loan deficiency payment based on a loan rate of $0.60 per pound
- Almost no detail on this program
- Leaving a lot to FSA to determine
Wool and Mohair Program
- Provides a marketing loan or loan deficiency payment based on a loan rate of:
- $1.00 per pound for graded wool
- $0.40 per pound for non-graded wool
- $4.20 per pound for mohair
- $0.40 per pound for unshorn pelts
Wool and Mohair Program (Cont.)
- Graded Wool
- Objectively measured by core test
- Fiber diameter and yield
- 2002 LDPs
- For wool, mohair shorn and sold before farm bill passed
- Keep sales receipt
- LDP aid based on date producer lost beneficial interest
- For wool, mohair shorn and sold before farm bill passed
- Almost no detail on this program
- Leaving a lot to FSA to determine
Dairy Program Provisions
- Maintains permanent price support at $9.90 per cwt
- Establishes 3.5 year counter-cyclical dairy program
- Monthly payments made to producers when the Boston Class I price falls below $16.94/cwt
- Producers would receive 45% of the difference between $16.94/cwt and the Boston Class I price
- Payments capped at 2.4 million pounds of milk per year (roughly the production from 135 to 140 cows)
- All producers on an operation could each receive benefits on 2.4 million pounds of milk
- Includes husbands, wives, siblings, etc
- Appears to be retroactive to Dec 31, 2001, ends September 30, 2005
- Continued dairy export incentive program (DEIP)
Percent of Production Eligible for Payment (Assuming 1 limit)

Conservation Program Changes
- Conservation Reserve Program
- Environmental Quality Incentives Program
- Conservation Security Program
- Others
- Wetlands Conservation Program
- Grasslands Reserve Program
Conservation Reserve Program
- Goal: Through the 2007 calendar year, CRP shall assist owners and operators of land to conserve and improve soil, water, and wildlife resources of such land.
- Increases acreage cap from 36.4 to 39.2 million acres
- Contracts expiring in 2002 may extend the contract for 1 additional year
- FSA data indicate that approximately 1,723,000 acres are under CRP contracts expiring 9/30/2002
- Retains priority areas
- Expands wetlands pilot to 1 million acres with all states eligible
Conservation Reserve Program (Cont.)
- Eligible land will include highly erodible cropland for which “the Secretary has determined a cropping history or was considered planted for 4 of the 6 years preceding the date of enactment of the Act.”
- Previously the requirement was 3 of the 5 years preceding the close of enrollment
Location of CRP Enrollment as of October 2000

Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP)
- To promote ag production and environmental quality as compatible goals, and to optimize environmental benefits (2002 – 2007)
- Very popular program
- Phased in increase in funding at:
2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007
Billion $ .4 1.0 1.0 1.2 1.2 1.3
- Funds to be split 60/40 between livestock and crops
- Cost-share and incentive payments
- 1 to 10 year contracts
- Payments limited to $450,000 per individual or entity over the duration of the contract(s)
EQIP (Continued)
- For 2002
- Texas had 11.5 million original allocation
- Received roughly 13 million more from 2002 farm bill
- Has to be obligated before September 30th
- Reopened signup until June 28th
- New applicants or changes to original applications
- Other Changes
- After this year, no more priority areas
- Eliminated buy downs
- Additional 6.6 million directed toward improved irrigation efficiency over Ogallala Aquifer
- Has to be obligated before September 30th
Conservation Security Program
- Establishes a new national incentive payment program for maintaining and increasing farm and ranch stewardship practices
- Begins in 2003 and runs through 2007
- Three Tiers (levels) of involvement I – III
- Tiers refer to length of contract and number of significant resource concerns addressed
- Annual payment limits
- Tier I – $20,000
- Tier II – $35,000
- Tier III – $45,000
- Nothing definite out on rules
- Apparently going to target resource concerns by county
Conservation Security Program (Cont.)
- Conservation Practices
- Nutrient management
- IPM
- Water conservation (including irrigation and water quality mgmt)
- Grazing, pasture, rangeland mgmt
- Soil conservation, quality, and residue mgmt
- Invasive species mgmt
- Fish and wildlife habitat conservation, restoration, and mgmt
- Air quality mgmt
- Energy conservation measures
- Biological resource conservation and regeneration
- Contour farming
- Strip cropping
- Cover cropping
- Controlled rotational grazing
- Resource-conserving crop rotation
- Conversion of portions of cropland from a soil depleting use to a soil-conserving use, including production of cover crops
- Depending upon county resource concerns
Other Conservation Programs
- Wetlands Reserve Program ($1.5 bil)
- Increases acreage cap to 2.275 million acres
- Permanent easements, 30-year easements, and restoration cost share agreements
- Grasslands Reserve Program ($254 mil)
- New program with 2.0 million acreage cap on restored or improved grassland, rangeland, and pastureland
- 10, 15, or 20 year rental agreements
- Wildlife Habitat Incentive Program ($700 mil)
- Cost-share payments to develop habitat
Miscellaneous
- Country of Origin Labeling
- Voluntary for 2002-2003, mandatory thereafter
- Meat, fish, produce, and peanuts by 2004
- For a product to be labeled a USA product, it must be born, raised, and processed in the U.S.
- 2 Loopholes:
- Does not include food service
- Does not include commodities that are ingredients in processed products
WTO Issues/Impacts
- Direct payments – green box (don’t count)
- MLGs/LDPs – commodity specific amber box
- CCPs – noncommodity specific amber box
- Amber Box limit is $19.1 billion annually
- Noncommodity specific support is not included when calculating the AMS as long as it is <5% of the value of agricultural production
- These amber box payments are referred to as “de minimus”
- If >5% then full amount counts
WTO Issues/Impacts (Cont.)
- Adjustment Authority Related to Uruguay Round Compliance
- If the Secretary determines expenditures will exceed allowable levels
- Contains provision to adjust expenditures
- If the Secretary determines expenditures will exceed allowable levels
What Do You Need to Do?
- Make sure you have all yields and acres certified
- If not, start getting together information you will need
- Become more acquainted with your choices
- Your local FSA office will be in touch
- Verify information they send you


Using BYA
- Resources You Can Access
- County Extension Agents
- Extension Management Specialists
- Usage So Far
- 37 Different States (TX, IA, IL, NE, KS, SD)
- The site has been accessed over 5000 times
- Software has been run
Issues on the Horizon
- National press having a hard time moving on to something else – spending
- Annual signup
- Conservation spending has a bulls eye on it
- Disaster assistance for 2001 and 2002 crops
- Payment limitations brought up in appropriations process
- This issue is far from settled
- Base updating in the future??
- Requirements to plant to receive payments??
Available Extension Resources
- Extension Economists
- County Extension Agents
- Website
- agecoext.tamu.edu
- Click on 2002 Farm Bill Educational Materials
- agecoext.tamu.edu
- Master Marketer
- FARM Assistance
Joe L. Outlaw
979-845-3062
joutlaw(at)tamu.edu